Solid solutions.
Partners for better care.
Our mission
We are partnering with healthcare professionals and manufacturers of innovative medical technologies, to deliver high-quality end-to-end solutions that enable better care.
News and Events
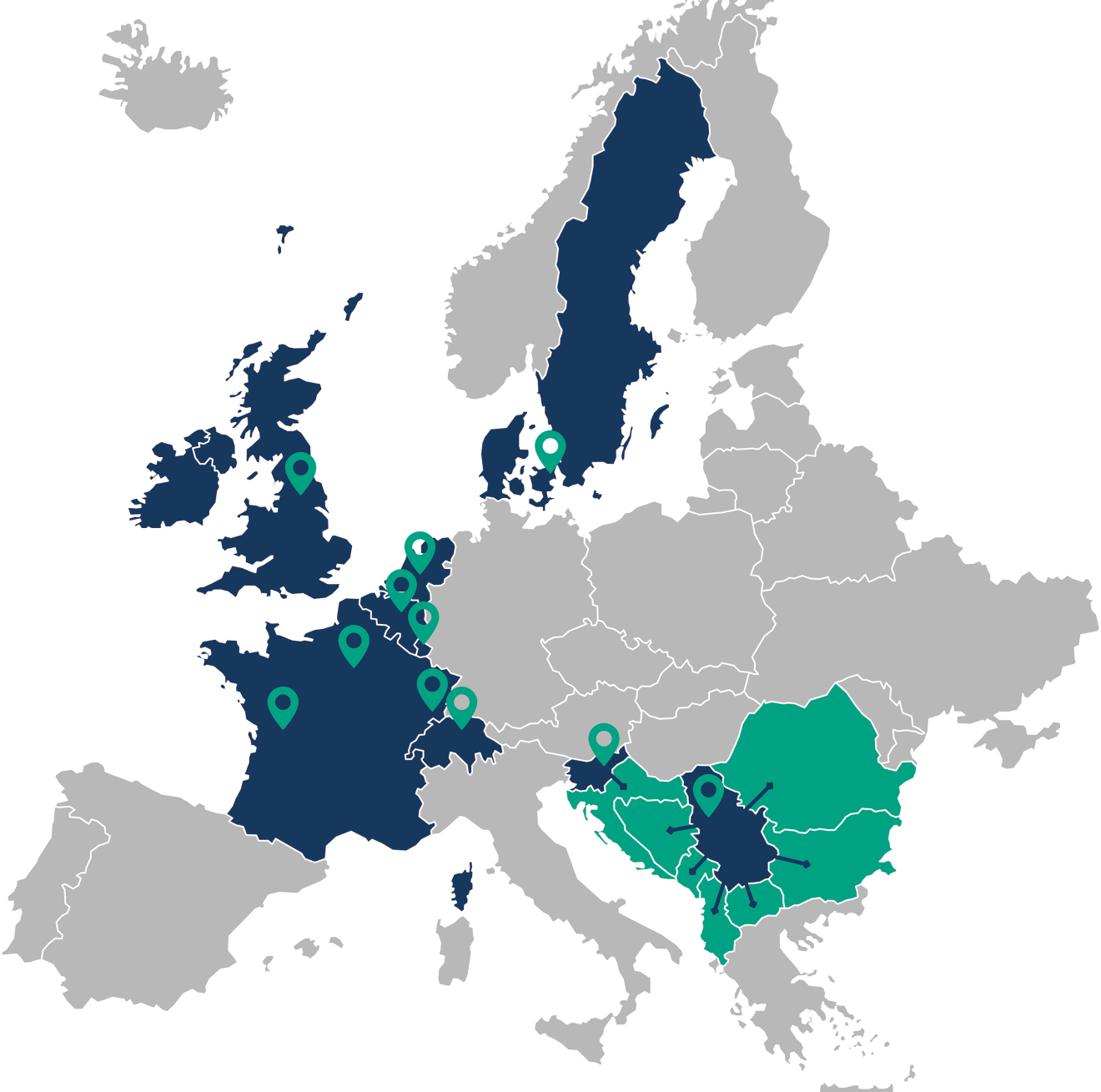
Part of the Duomed Group
Solid solutions. Partners for better care.
The Duomed Group is a dynamic organization with a well-established reputation and is active in consultancy, sales, integration, training and technical support of medical technology and devices for hospitals and medical practices.
We are partnering with healthcare professionals and manufacturers of innovative medical technologies, to deliver high-quality end-to-end solutions that enable better care.
Our group is in full growth and is active in Belgium, The Netherlands, Luxembourg, France, Denmark, Sweden, Switzerland, the UK and Southeast Europe.